Blockchain Smart Contracts Explained A Comprehensive Guide
As blockchain smart contracts explained takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world filled with innovation and potential. Smart contracts, integral to blockchain technology, automate processes and enhance trust in digital transactions. Understanding their origins and evolution opens up a conversation about their transformative role in the modern economy.
These self-executing contracts contain the terms of the agreement directly written into code, enabling them to operate without intermediaries. The interplay between security and efficiency that blockchain offers enhances the reliability of these contracts, making them a pivotal element in various industries.
Introduction to Blockchain Smart Contracts
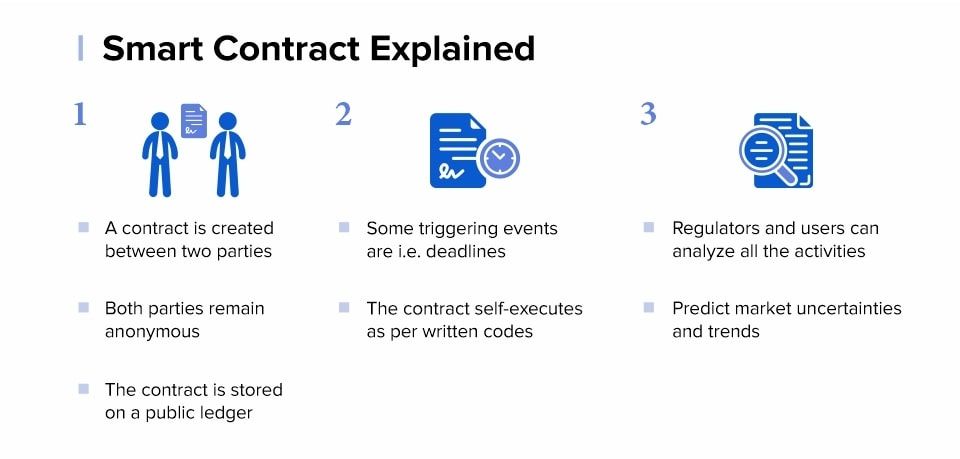
Smart contracts are a revolutionary aspect of blockchain technology, allowing for self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This innovative approach eliminates the need for intermediaries, making transactions faster, cheaper, and more secure. The history of smart contracts dates back to the early '90s when computer scientist Nick Szabo introduced the concept, but it gained substantial traction with the advent of blockchain platforms like Ethereum.
Today, smart contracts play a vital role in the digital economy by enabling automated processes and reducing the friction associated with traditional contract management.
History and Evolution of Smart Contracts
The idea of smart contracts was first proposed by Nick Szabo in 1994, aiming to bring automation and reliability to contractual agreements. With the rise of blockchain technology, particularly Ethereum in 2015 which fortified the concept, smart contracts became more than just a theoretical idea. This development allowed developers to create decentralized applications (dApps) that could operate without intermediate parties.
The significance of smart contracts in the digital economy is profound, as they facilitate trustless transactions, thereby broadening access to markets and democratizing opportunities.
Significance of Smart Contracts in the Digital Economy

Smart contracts contribute significantly to the digital economy by:
- Reducing transaction costs by eliminating intermediaries.
- Enhancing efficiency through automated processes that execute once conditions are met.
- Increasing accessibility to services and resources, enabling more participants in various markets.
How Blockchain Smart Contracts Work
Smart contracts operate on blockchain networks, where they are executed and enforced by the consensus of the network participants. The mechanics behind executing a smart contract involve several steps, including creating the contract code, deploying it on the blockchain, and executing conditions based on predefined rules.
Mechanics of Executing a Smart Contract
The execution of a smart contract begins when a triggering event occurs. This could be anything from a specific date to a transaction. Once triggered, the contract code is executed across all nodes in the network, ensuring transparency and immutability. Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and trust of smart contracts, as it provides a decentralized ledger that is resistant to tampering and fraud.
Writing and Deploying Smart Contracts
Developers typically write smart contracts using programming languages like Solidity for Ethereum. After coding, the smart contract must be tested rigorously before deployment to mitigate bugs and vulnerabilities. Once verified, it is deployed to the blockchain where it lives permanently, ready to execute when conditions are met.
Advantages of Using Smart Contracts
The adoption of smart contracts across various industries brings a plethora of advantages, making them an attractive option for businesses and individuals alike.
Benefits of Utilizing Smart Contracts

Smart contracts offer multiple benefits, including:
- Cost savings from reduced administrative overhead and elimination of intermediaries.
- Increased efficiency through the automation of processes and quicker transaction times.
- Enhanced transparency, as all parties have access to the same immutable data.
- Reduction in fraud due to the secure nature of blockchain technology.
Cost Savings and Efficiency Improvements
Various industries have experienced cost savings and efficiency improvements through smart contracts. For instance, in supply chain management, smart contracts streamline the tracking of goods and payment processes, leading to significant reductions in delays and discrepancies. Additionally, the real estate sector utilizes smart contracts to automate property transfers and reduce closing costs.
Challenges and Limitations of Smart Contracts
Despite their advantages, smart contracts are not without challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for broader adoption.
Legal and Regulatory Issues
Smart contracts often face legal and regulatory uncertainties as they exist in a gray area in many jurisdictions. This can lead to complications regarding enforceability and dispute resolution, as traditional legal systems may not be equipped to handle blockchain-based agreements.
Technical Challenges
From a technical standpoint, coding smart contracts requires precise programming skills. Bugs or vulnerabilities in the code can lead to significant financial losses. Integration with existing systems can also pose challenges, as legacy systems may not easily accommodate blockchain technology.
Scenarios Where Smart Contracts May Not Be the Best Solution
There are specific scenarios where smart contracts may not be ideal, such as complex agreements requiring nuanced understanding and judgment. In cases involving subjective criteria or significant human discretion, traditional contracts may be more effective.
Real-World Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are currently being utilized across various sectors, showcasing their practical applications and benefits.
Industries Utilizing Smart Contracts Effectively
Several industries have adopted smart contracts, including:
- Finance: Automated loan agreements and secure transactions.
- Healthcare: Secure sharing of patient data and automated billing.
- Gaming: In-game purchases and asset ownership verification.
Case Studies of Successful Implementation
One notable example is the use of smart contracts in supply chain management by companies like Walmart and IBM, which utilize blockchain technology to track product journeys from origin to retail, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Future of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
The future of smart contracts holds exciting potential, with emerging trends likely to shape their development and usage.
Emerging Trends and Potential Developments
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, smart contracts will benefit from advancements in scalability, interoperability, and user-friendliness. This may include improvements in programming languages and platforms that make it easier for developers to create robust smart contracts.
Influence of Advancements in Technology
Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning could integrate with smart contracts, enabling more complex and adaptive contract executions based on real-time data analysis. This could lead to even greater efficiencies and new applications in various sectors.
Broader Societal Impacts of Smart Contracts
The widespread adoption of smart contracts could lead to more democratized access to services, reduced reliance on traditional financial institutions, and a shift in how trust is established in transactions, ultimately transforming societal interactions in the digital age.
Best Practices for Developing Smart Contracts
To ensure the effectiveness and security of smart contracts, developers should adhere to certain best practices.
Checklist for Robust Smart Contract Coding
A robust smart contract should include:
- Clear and concise code that is easy to understand and audit.
- Thorough documentation detailing the contract's purpose and functionalities.
- Incorporation of security measures to prevent vulnerabilities and exploits.
Guidelines for Testing and Auditing
Before deployment, smart contracts should undergo extensive testing, including unit tests and integration tests. Engaging third-party auditors to review the code can also help identify potential issues.
Importance of Ongoing Maintenance and Updates
After deployment, continuous monitoring and updates are essential to address any emerging vulnerabilities or to improve functionalities based on user feedback. This ensures that smart contracts remain effective and secure over time.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain smart contracts represent a significant leap forward in how agreements are formed and fulfilled. Their advantages, from cost savings to increased transparency, are compelling, yet it's essential to navigate the challenges they present. As we look to the future, ongoing advancements in technology are likely to further refine smart contracts, potentially reshaping societal interactions and the landscape of commerce.
FAQ Overview
What are blockchain smart contracts?
Blockchain smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code on a blockchain.
How do smart contracts ensure security?
Smart contracts use cryptographic algorithms and the decentralized nature of blockchain to ensure data integrity and prevent tampering.
Can smart contracts be modified after deployment?
Typically, smart contracts are immutable once deployed; however, some designs allow for upgrades through specific mechanisms.
What industries benefit from smart contracts?
A variety of sectors, including finance, real estate, and supply chain management, are leveraging smart contracts for efficiency and transparency.
What are the legal implications of smart contracts?
Legal recognition of smart contracts varies by jurisdiction, which can complicate enforcement and compliance with existing laws.


